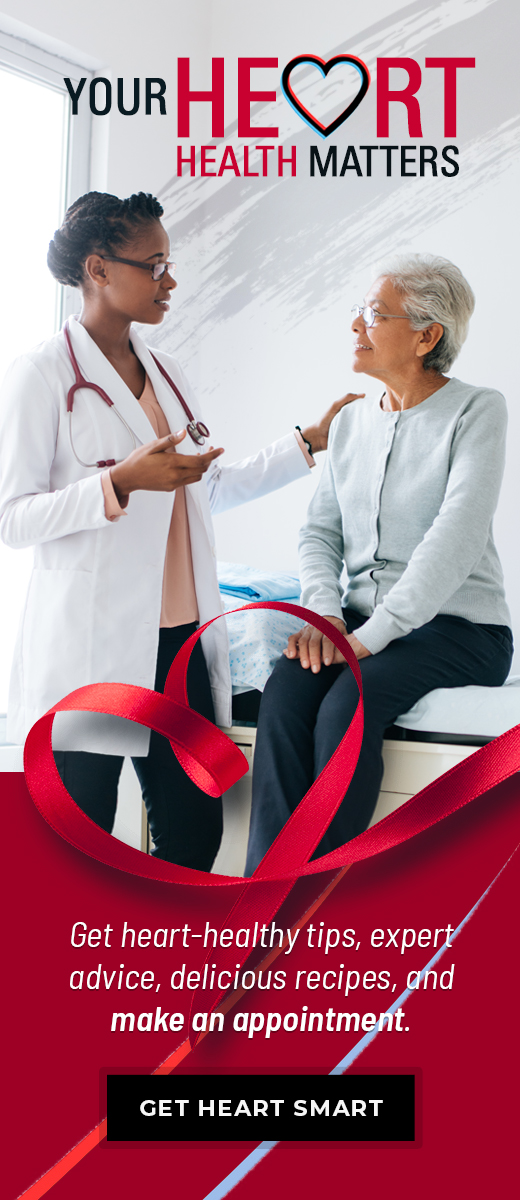
These breakfast bites are the perfect, pop-able, protein filled, gluten-free breakfast. Easy, delicious and can be enjoyed by the whole family.
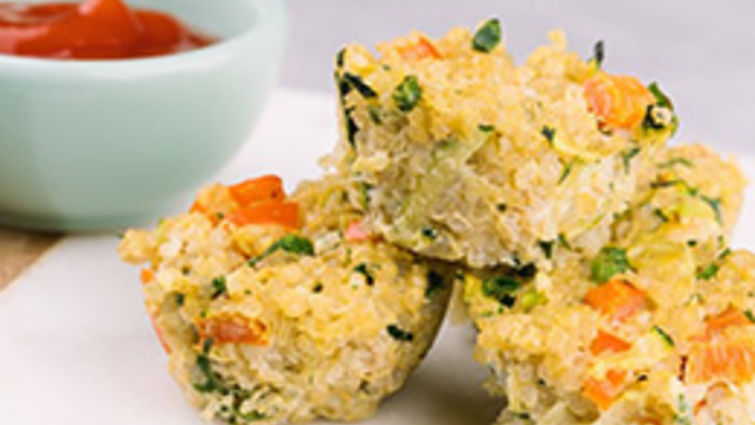

Recipe: Quinoa Breakfast Bites
Serving size: 4 mini cups
Servings per recipe: 7
Prep time: 15 min
Cook time: 20 min
- 2 cups - Quinoa, cooked (3/4 uncooked for reference)
- 2 ea - Large eggs + 2 egg whites
- 1 cup - Zucchini, shredded and squeezed dry
- 1/4 cup - Cheese, shredded (your choice of cheese)
- 1/4 cup - Parsley, minced
- 2 ea - Green onions, sliced
- 1 medium - Red bell pepper, small diced
- Season to taste
Directions
Preheat oven to 350°F. In a large bowl, whip eggs thoroughly, then add in cooked quinoa, zucchini pressed dry, cheese, parsley, green onions and bell pepper. Mix well. Grease mini* muffin pan liberally. Spoon mixture to pan, using about 1 heaping tablespoon per cup. Bake 15-20 minutes or until edges start to brown. Let cool before removing from pan.
Freezer instructions: Place baked and cooled breakfast bites on a baking sheet until frozen, then transfer to a freezer safe bag. Microwave 20-40 seconds to thaw.
*For regular size muffin pan, cook 25-30 minutes or until the edges start to brown.
Nutrition Facts
Serving size:
| Calories | 126 |
| Carbohydrates | 13g |
| Fiber | 2g |
| Total Fat | 5g |
| Saturated Fat | 2g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 2g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 1g |
| Sodium | 90mg |
| Protein | 7g |
| Sugar | 1g |
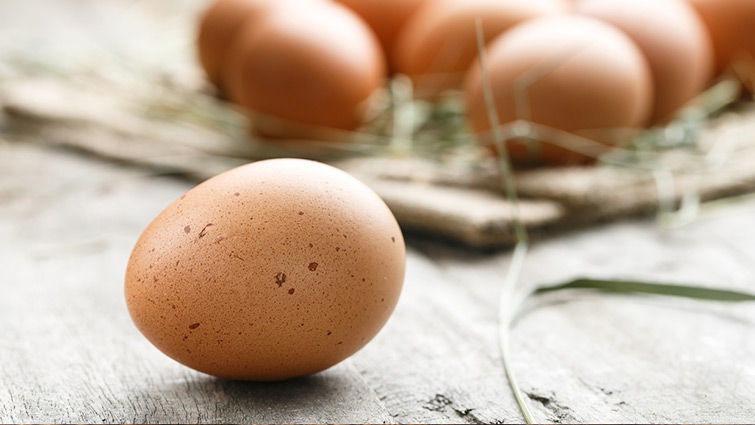

Star Ingredient:
Eggs Contain:
Selenium 3*
Selenium is an essential trace mineral. It is part of an antioxidant enzyme called glutathione peroxidase which prevents the free-radical formation, thus blocking the damaging chain. Selenium also plays a role in converting the hormone to its active form. The risk of deficiency is very low. Anyone who eats a normal diet composed mostly of unprocessed foods need not worry about meeting the selenium recommendations. Selenium is widely distributed in foods such as meats, shellfish and vegetables and grains grown in selenium-rich soil.
Omega 6 Fatty Acids*
The human body can synthesize all the fatty acids it needs from carbohydrate, fat or protein except for two, linoleic and linolenic acid.
Linoleic acid is an Omega-6 fatty acid found in the seeds of plants and in the oils produced from the seeds. Any diet that contains vegetable oils, seeds, nuts and whole grain foods provides enough linoleic acids to meet the body’s needs. From this essential fatty acid, the body makes important hormone-like substances that help regulate a wide range of body functions: blood pressure, clot formation, blood lipid concentration, the immune response, the inflammatory response to injuries and many others.
Vitamin D*
When most think of vitamin D, they automatically think of the sun. The body can synthesize it with the help of sunlight. Therefore, vitamin D is not an essential nutrient. Given enough sun, people don't need vitamin D from foods. If not enough sunlight, there are a few animal foods such as eggs, liver, butter and some fish, along with fortified milk that provides significant amounts of vitamin D. Although called a vitamin, it is actually a hormone – a compound manufactured by one organ of the body that has effects on another. The best-known vitamin D targeted organs are the intestine, the kidneys, and the bones. Vitamin D’s special in the role in bone growth is to make calcium and phosphorus available in the blood that bathes the bones.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.